[모두를 위한 딥러닝2 Pytorch] Softmax Classification
🍳 reference: <모두를 위한 딥러닝 2: pytorch> Lab6
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
Softmax
soft하게 max값을 뽑아주는 함수
z = torch.FloatTensor([1, 2, 3])
hypothesis = F.softmax(z, dim=0)
print(hypothesis)
# tensor([0.0900, 0.2447, 0.6652])
원래 max는 0,0,1을 출력하지만 softmax는 합쳐서 1이 되도록 출력함
Cross Entropy
두 확률 분포가 얼마나 비슷한지를 나타내는 함수
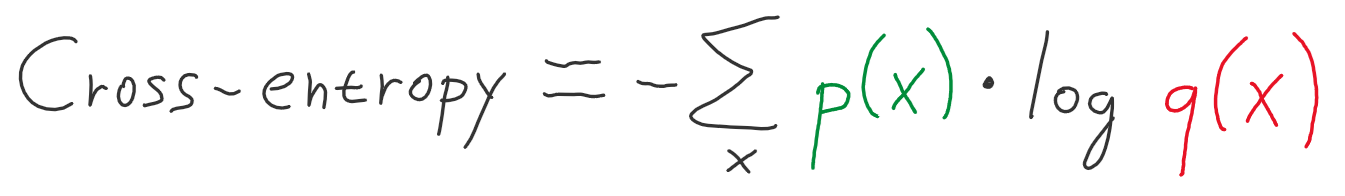
cross entropy loss
z = torch.rand(3, 5, requires_grad=True) # 3개의 sample, 5개의 class
hypothesis = F.softmax(z, dim=1)
print(hypothesis)
#tensor([[0.2645, 0.1639, 0.1855, 0.2585, 0.1277],
# [0.2430, 0.1624, 0.2322, 0.1930, 0.1694],
# [0.2226, 0.1986, 0.2326, 0.1594, 0.1868]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
discret 하므로, 이를 one-hot vector로 표현해주자
y_one_hot = torch.zeros_like(hypothesis)
y_one_hot.scatter_(1, y.unsqueeze(1), 1) # 각각 dim = 1에 대해, y.unsqueeze(1)에 1을 뿌리기
### 즉, [0,2,1]이 아래와 같이 변함
#tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.]])
cost = (y_one_hot * -torch.log(hypothesis)).sum(dim=1).mean()
print(cost)
# tensor(1.4689, grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
위에서, -torch.log(hypothesis))는 (3,5)이지만, sum(dim=1)을 적용함으로서 (3,)이 됨
이후 mean()의 결과 하나의 숫자로 결과를 반환
model.nn 을 이용하면 아래와 같다
# Low level
torch.log(F.softmax(z, dim=1))
# High level
F.log_softmax(z, dim=1)
또한 log Likelyhood는
# Low level
(y_one_hot * -torch.log(F.softmax(z, dim=1))).sum(dim=1).mean()
# tensor(1.4689, grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
# High level
F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(z, dim=1), y)
#tensor(1.4689, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward>)
이때 NLL은 Negative Log Likelyhood 이다.
그러나 cross_entropy() 를 이용하면 softmax와 NLL을 모두 한번에 처리할 수 있다
F.cross_entropy(z, y)
#tensor(1.4689, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward>)
Implementation
전체 학습 코드는 아래와 같다.
아래의 경우는 m개의 sample, 3개의 class, 4-dimension 이다.
x_train = [[1, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 3, 2],
[3, 1, 3, 4],
[4, 1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5, 5],
[1, 2, 5, 6],
[1, 6, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7, 7]]
y_train = [2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_train)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train)
# 모델 초기화
W = torch.zeros((4, 3), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
# optimizer 설정
optimizer = optim.SGD([W, b], lr=0.1)
nb_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
# Cost 계산 (1)
hypothesis = F.softmax(x_train.matmul(W) + b, dim=1) # or .mm or @
y_one_hot = torch.zeros_like(hypothesis)
y_one_hot.scatter_(1, y_train.unsqueeze(1), 1)
cost = (y_one_hot * -torch.log(F.softmax(hypothesis, dim=1))).sum(dim=1).mean()
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 100번마다 로그 출력
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))
위에서 Cost 계산 부분만 아래 코드로 대체 가능하다
# Cost 계산 (2)
z = x_train.matmul(W) + b # or .mm or @
cost = F.cross_entropy(z, y_train)
또는 SoftmaxClassifierModel()를 사용하면 아래와 같다
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
# optimizer 설정
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
nb_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
# H(x) 계산
prediction = model(x_train)
# cost 계산
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_train)
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 20번마다 로그 출력
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))