🍳 reference: <모두를 위한 딥러닝 2: pytorch> Lab7-1
Maximum Likelyhood Estimation(MLE)
data observation를 가장 잘 설명할 수 있는 parameter를 찾는 과정이다.
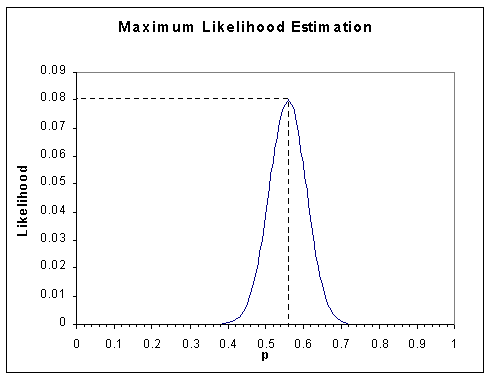
위 그래프에서는 볼록하게 높은 부분 즉, p= 0.56인 지점을 찾아야 한다.
이를 위해서는 기울기를 이용하는데, 최대를 찾기 위해 gradient ascent를 사용하거나 최소를 찾기 위해 gradient descent를 사용한다.

overfitting
다만, MLE는 overfitting을 피할 수 없는데,
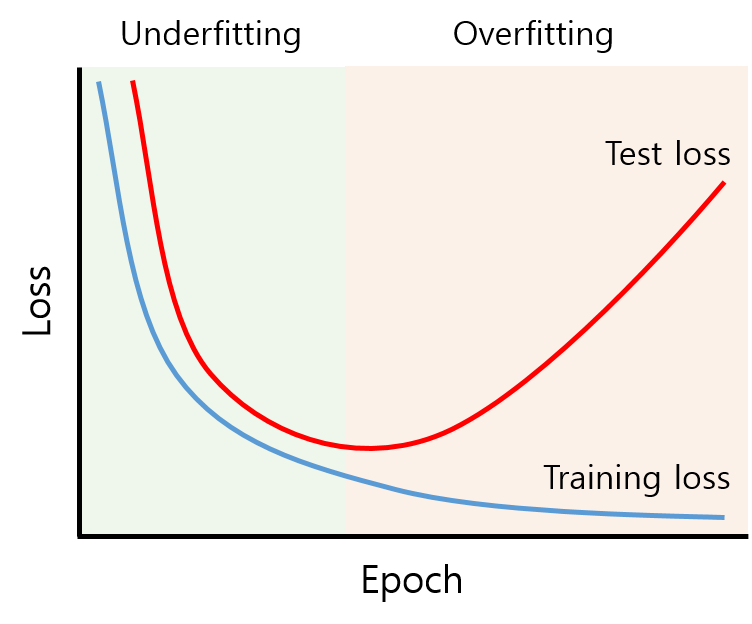
위와 같은 그래프를 그려 만약 train loss는 감소하는데 비해 validation loss는 그대로이거나 증가한다면 overfitting을 의심가능하다.
overfitting을 막기 위해
더 많은 data를 사용하거나, feature를 줄이거나, regularization을 사용한다
regularization은 early stopping, network size 줄이기, weight 크기 제한 (decay), dropout, batch normalization 등등이 있다.
전체적인 flow는 아래와 같다
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2, 1],
[1, 3, 2],
[1, 3, 4],
[1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5],
[1, 2, 5],
[1, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7]
])
y_train = torch.LongTensor([2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0])
x_test = torch.FloatTensor([[2, 1, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 3, 4]])
y_test = torch.LongTensor([2, 2, 2])
'''
class SoftmaxClassifierModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(3, 3)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
def train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train):
nb_epochs = 20
for epoch in range(nb_epochs):
# H(x) 계산
prediction = model(x_train)
# cost 계산
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_train)
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))
def test(model, optimizer, x_test, y_test):
prediction = model(x_test)
predicted_classes = prediction.max(1)[1]
correct_count = (predicted_classes == y_test).sum().item()
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_test)
print('Accuracy: {}% Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
correct_count / len(y_test) * 100, cost.item()
))
'''
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
train(model, optimizer, x_train, y_train)
test(model, optimizer, x_test, y_test)
Learning rate
learning rate가 너무 크면 diverge하면서 cost가 점점 늘어날수도 있다 (overshooting )
너무 작으면 cost가 거의 줄어들지 않는다.
따라서 적절한 숫자로 시작해 작게 조정하고, 만약 cost가 줄어들지 않으면 크게 조정하자.
Data Preprocessing
전처리 과정을 거치면 더 정확한 학습, 예측 가능
e.g. zero-center하고 normalize하기 (정규 분포로 만들기)
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[73, 80, 75],
[93, 88, 93],
[89, 91, 90],
[96, 98, 100],
[73, 66, 70]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[152], [185], [180], [196], [142]])
mu = x_train.mean(dim=0)
sigma = x_train.std(dim=0)
norm_x_train = (x_train - mu) / sigma