🍳 reference: <모두를 위한 딥러닝 2: pytorch> Lab11
물론 아직 CNN 강의를 다 들은 건 아니지만 사정상 RNN을 먼저 보기로 했다!
RNN
RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)은 입력과 출력을 sequence 단위로 처리하는 모델이다.
즉 word, text, time series 와 같이 순서가 중요한(순서도 data의 일부가 되는) sequential data에 대해 적당하기에, NLP 에서도 많이 쓰인다.
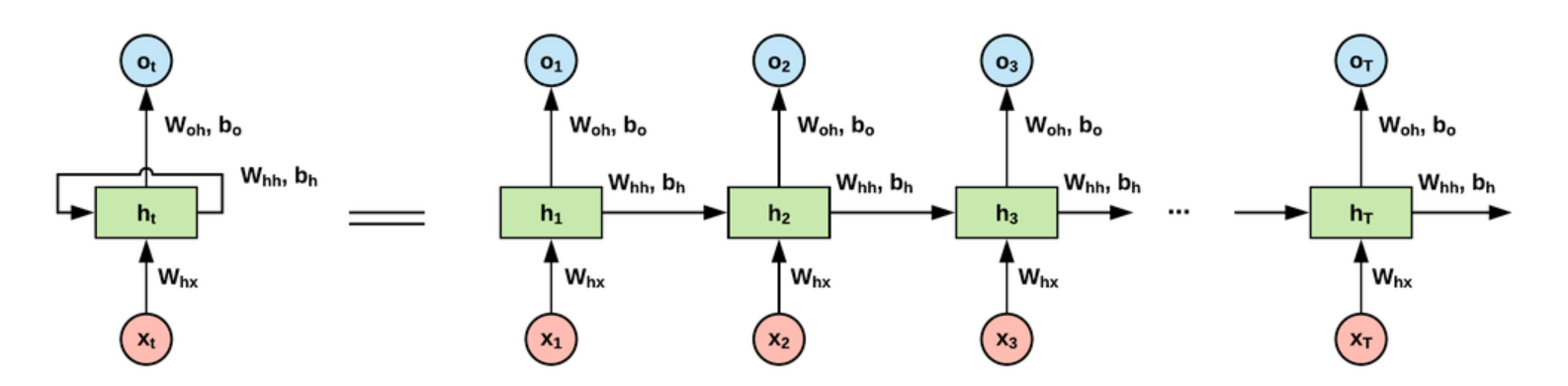

RNN의 hidden state 덕분에 전 단계의 node에서의 결과값을 현 단계의 node에 반영할 수 있고
모든 cell이 전부 parameter를 공유하기에 sequential data에 적당한 것이다.
one-to-one 부터 many-to-many는 이미 배운거라 일단 넘기기!
직접 RNN을 구동하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
물론 character(letter) 단위로도 가능하지만,글자 (charseq) 단위로 진행해보려 한다.
예제 문장은 ‘if you want you’ 이다.
문자 if you want you를 모델이 인식할 수 있도록 encoding 하는 과정이 필요한데,
이 코드에서는 one-hot encoding을 이용했다.
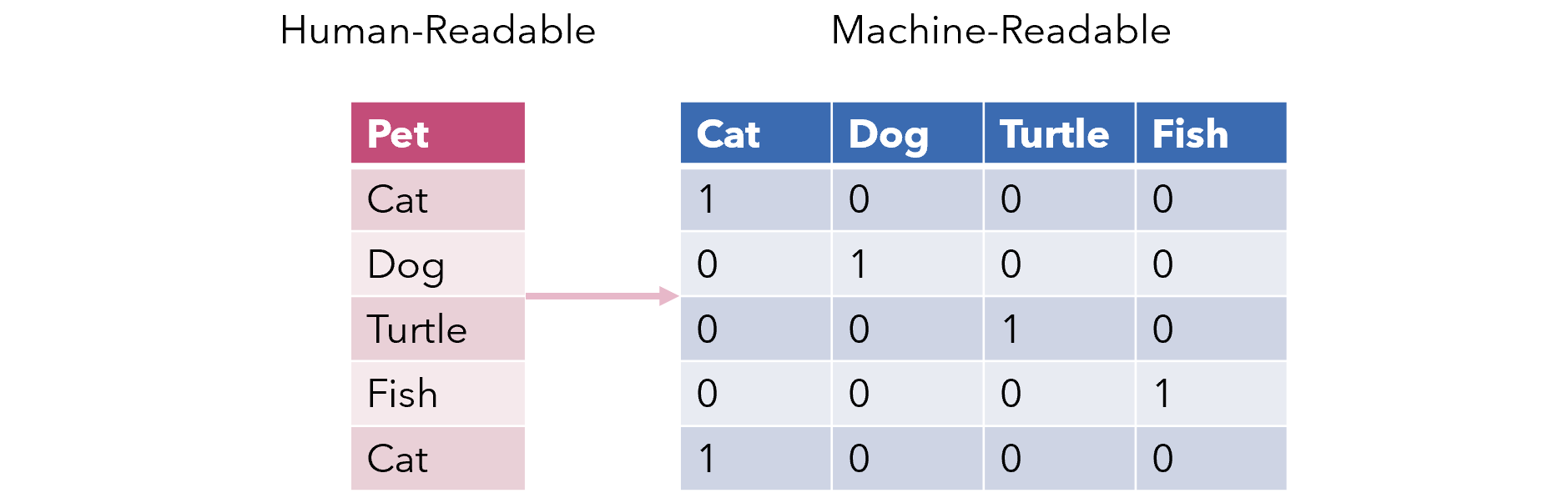
입력에 들어가기 위해서는 알맞은 tensor manipulation을 거쳐야 한다.
이때, pytorch에서의 표현은 ( _, _, _) 이렇게 되는데,
앞자리는 batch size,
중간 자리는 letter 또는 char의 자리수,
마지막 자리는 input data의 경우 input의 letter 종류 (이 경우 단어의 종류)의 개수 즉 dimension 개수이고,
output data의 경우 hidden size와 동일하다.
예를 들어 input data가 ‘hello’ 이고 hidden size = 2, batch size = 3인 경우,
input shape = (3, 5, 4), output shape = (3, 5, 2) 이다.
아래의 경우 X.shape은 [1, 14, 10]이고, y.shape은 [1, 14]이다.
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
sample = "if you want you"
# make dictionary
char_set = list(set(sample))
char_dic = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(char_set)}
char_dic을 출력하면 아래와 같다.
{' ': 8,
'a': 3,
'f': 0,
'i': 7,
'n': 1,
'o': 6,
't': 9,
'u': 5,
'w': 2,
'y': 4}
즉 길이가 10개인 dictionary가 만들어진 셈이다.
따라서 input data shape의 마지막 자리수는 10이다.
아래를 보면, 이 모델에선 hidden size도 10으로 지정한다.
또한 encoding 결과, 14개의 결과가 나오기 때문에 두번째 자리수는 14이다.
# hyper parameters
dic_size = len(char_dic)
hidden_size = len(char_dic)
learning_rate = 0.1
sample_idx = [char_dic[c] for c in sample]
x_data = [sample_idx[:-1]]
x_one_hot = [np.eye(dic_size)[x] for x in x_data]
y_data = [sample_idx[1:]]
X = torch.FloatTensor(x_one_hot)
Y = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# declare RNN
rnn = torch.nn.RNN(dic_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
# loss & optimizer setting
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), learning_rate)
# start training
for i in range(50):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs, _status = rnn(X)
loss = criterion(outputs.view(-1, dic_size), Y.view(-1))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
result = outputs.data.numpy().argmax(axis=2)
result_str = ''.join([char_set[c] for c in np.squeeze(result)])
print(i, "loss: ", loss.item(), "prediction: ", result, "true Y: ", y_data, "prediction str: ", result_str)