* 요약
- BART란? Seq-to-Seq model을 pre-training 하기 위한 denoising autoencoder
- denoising autoencoder ; 잡음을 제거하는 autoencoder
- autoencoder의 진화형
-
autoencoder ; 입출력이 동일한 네트워크 (encoder는 input data의 주요 feature를 압축된 형태로 추출하고, decoder는 그것을 다시 복원함)
-
Input Data를 Encoder Network에 통과시켜 압축된 z값을 얻음
→ 압축된 z vector로부터 Input Data와 같은 크기의 출력 값을 생성 (이때 Loss값은 입력값 x와 Decoder를 통과한 y값의 차이)
- Input Data의 Feature를 추출할 때 많이 사용됨
- 학습 방법
- Decoder Network를 통과한 Output layer의 출력 값은 Input값의 크기와 같아야 함
- 이때 학습을 위해서는 출력 값과 입력값이 같아져야 함
-
- denoising autoencoder ; 잡음을 제거하는 autoencoder
- seq-to-seq ; **한 문장(시퀀스)을 다른 문장(시퀀스)으로 변환하는 모델로,** 기계 번역, 문장 생성, 질의응답, 메일 자동 응답 등에 활용됨
- 나는 그곳에 갔다 -> I there went 가 아니라, I went there로 번역됨 - BART는 다음과 같이 학습됨
(1) corrupting text with an arbitrary noising function.
(2) learning a model to reconstruct the original text.
- standard Transformer 기반의 neural machine translation architecture를 사용
1. Introduction
- masking이 성능 향상에 기여했음을 언급
- masking된 token의 순서를 예측하는 것과, masking된 token에 적절한 context를 대체하는 것 등등
- 본 논문에서는 BART(Bidirectional and Auto-Regressive Transformers)를 제안;
- Bidirectional Transformer와 Auto-Regressive Transformers를 결합한 모델로 pre-train함
-
두가지 단계로 pre-train함
1) 임의의 noising function으로 text를 망가뜨림(이때, length도 변함)
- 이러한 denoising approach를 다양하게 사용해본 결과, random shuffling이랑 in-filling scheme이 제일 좋았음
2) seq-to-seq model이 원래의 text로 복구하도록 학습됨
→ 모델 코드를 직접 보고싶음 !!
-
denoising autoencoder임;
-
- 기존의 방법들이 특정 type의 end task만 초점을 둔 데에 비해, BART는 다양한 범위의 end task 가능
- text generation으로 fine-tuning되었지만, comprehension task도 가능 (SOTA 달성)
- standard Transformer-based neural machine translation architecture임
- BERT의 encoder와, GPT2의 decoder를 따왔음 (사실 각각은 transformer의 encoder, decoder이긴 함)
- BERT에서, 각각의 masking token은 별도로 예측되므로 text generation에는 적절하지 않음
- GPT에서, 각 token은 auto-regressive하게 예측하지만, bidirectional하지 않음
- Bidirectional Transformer와 Auto-Regressive Transformers를 결합한 모델로 pre-train함
2. Model
negative log-likelihood로 optimization
2.1. Architecture
- seq-to-seq Transformer architecture model사용
- encoder, decoder 각각 6 layer (large 버전은 12 lyer)
- BERT와의 차이 2가지
- BART의 decoder의 각 layer는, encoder의 마지막 hidden layer에 대해 cross-attention을 수행함
- BART와 달리, BERT는 word prediction 이전에 추가적인 feed-forward network를 가짐
→ BART의 parameter가, 동일한 크기의 BERT보다 10% 많음
2.2. Pre-Training BART
- BART는, 망가뜨린 text를 복원하는 loss를 optimizing하며 학습함
- 원래 text와, BART가 만들어낸 output과의 cross-entropy사용
- 기존의 denoising autoencoder와 달리, 어떤 종류의 document corruption도 사용 가능
- 사용한 transformer들
- token masking; BERT처럼, random token을 masking([MASK]로 대체함)
- token deletion; token masking과 달리, input중에 랜덤으로 token을 삭제함
-
text infilling; text span을 sampling하여 하나의 단어([MASK])로 masking하거나, [MASK]를 사이에 넣음. (SpanBERT와 달리, masking을 통해 길이가 달라짐)
→ 얼마나 많은 token이 span에서 없어졌는지를 예측하도록
- sentence permutation
-
document rotation; random token을 추려서, document가 해당 token으로 시작하도록 만듦
→ document가 어떤 단어로 시작하는지를 예측하도록
3. Fine-tuning BART
다양한 downstream task에 BART를 적용 가능
3.1. Sequence Classification Tasks
- encoder, decoder에 같은 input이 들어가고, final decoder token의 final hidden state가 new multi-class linear classifier로 들어감
- BERT의 CLS처럼, 맨 마지막에 ‘end’를 추가함; decoder의 token represenation이 input의 끝을 알 수 있도록
3.2. Token Classification Tasks
- e.g. SQuAD
- encoder, decoder에 complete document가 들어가고, decoder의 top hidden state가 각 단어의 representation으로 사용됨
3.3. Sequence Generation Tasks
- abstract QA, summarization
- BART가 auto-regressive decoder라서, Sequence Generation Tasks로 바로 fine-tuning됨
3.4 Machine Translation
- BART를 기계번역의 단일 Decoder로 사용가능
- BART의 encoder embedding layer를 randomly initialized encoder로 교체 가능; original BART model로부터 seperate vocab사용 가능
4. Comparing Pre-training Objectives
pre-train, downstream task에서 사용되는 다양한 noising scheme비교 (with base-size model)
4.1. Comparison Objectives
- objective function을 비교하는 건 쉽지 않음
- training data, training resource, 구조적 차이 , fine-tuning procedual에 따라 다르기 때문 ,,,
→ 최대한 노력했다!
- 비교 내용들
- language model ; GPT와 비슷
- permutated language model ; XLNet base
- masked language model ; BERT
- multitask masked language model ; UniLM
- masked seq-to-seq ; BART
4.2. Tasks
- SQuAD(QA), MNLI(bitext classification), ELI5(QA), XSum(summarization), ConvAI2(dialogue), CNN/DM(summarization)
4.3. Results
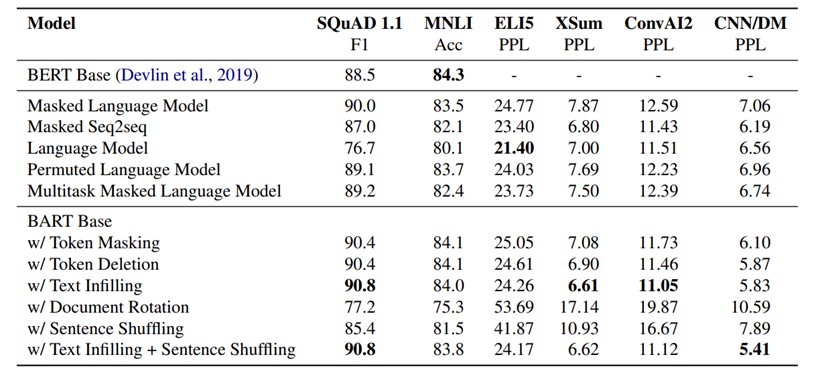
- Performance of pre-training methods varies significantly across tasks
- Token masking is crucial
- Left-to-right pre-training improves generation
- Bidirectional encoders are crucial for SQuAD
- The pre-training objective is not the only important factor
- Pure language models perform best on ELI5
- BART achieves the most consistently strong performance.
5. Large-scale Pre-training Experiments
RoBERTa와 같은 크기가 되도록, large-scale pre-training진행
6. Qualitative Analysis
- BART가 큰 성능 향상을 보인 text summarization에 대한 분석
- copied phrase가 거의 없고, 문법도 잘 맞으며, 잘 요약되어 있음
→ BART pre-training이 NLU, NLG를 잘 하고 있음을 확인 가능